Neuropop Example¶
A demonstration of Neuropop using simulated data
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from spykes.ml.neuropop import NeuroPop
from spykes.utils import train_test_split
Create a NeuroPop object¶
n_neurons = 10
pop = NeuroPop(n_neurons=n_neurons, tunemodel='glm')
Simulate a population of neurons¶
n_samples = 1000
x, Y, mu, k0, k, g, b = pop.simulate(pop.tunemodel, n_samples=n_samples,
winsize=400.0)
Split into training and testing sets¶
np.random.seed(42)
(Y_train, Y_test), (x_train, x_test) = train_test_split(Y, x, percent=0.5)
Fit the tuning curves with gradient descent¶
pop.fit(x_train, Y_train)
Predict the population activity with the fit tuning curves¶
Yhat_test = pop.predict(x_test)
Score the prediction¶
Ynull = np.mean(Y_train, axis=0)
pseudo_R2 = pop.score(Y_test, Yhat_test, Ynull, method='pseudo_R2')
print(pseudo_R2)
Out:
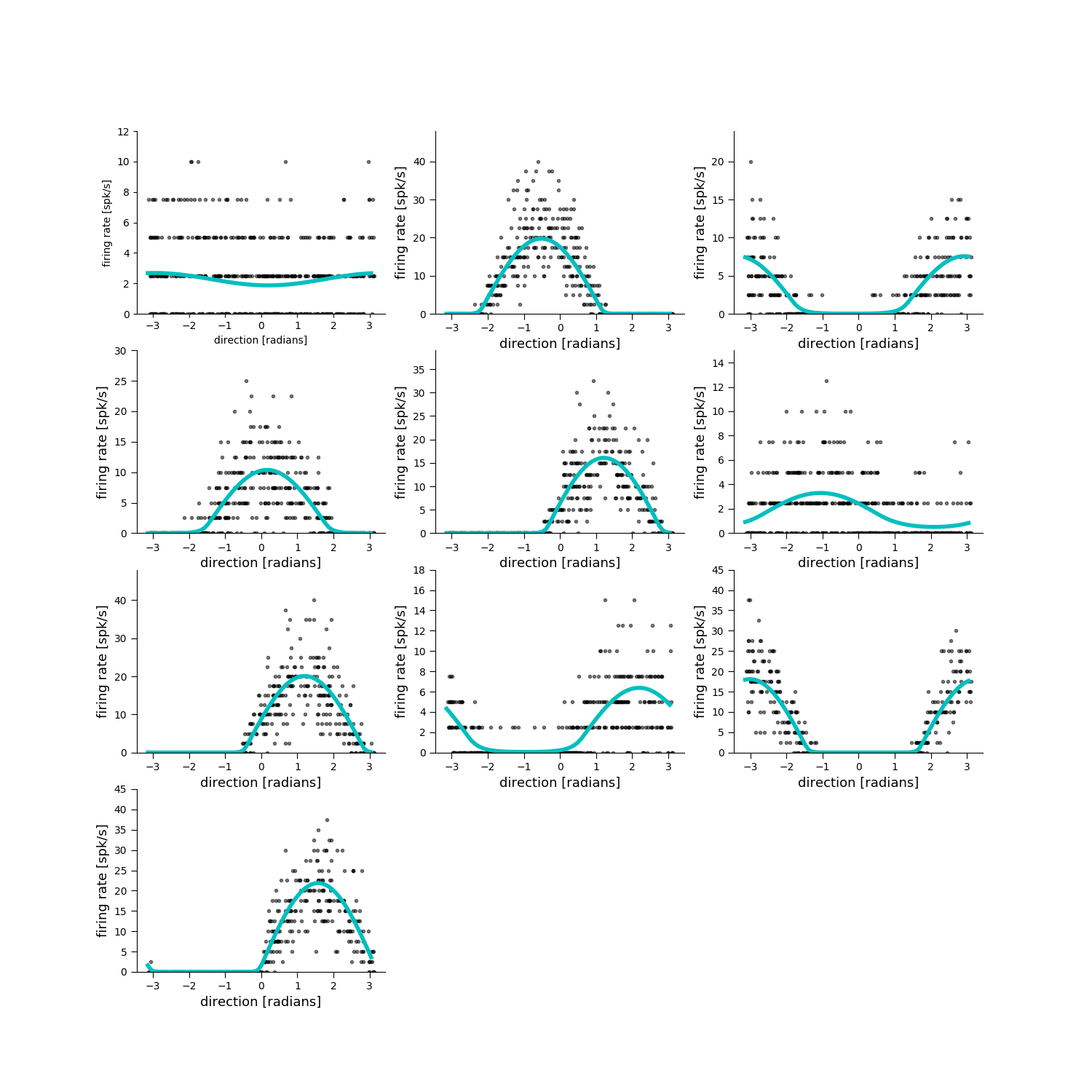
[0.012898436115752809, 0.87906982333904071, 0.64953551355040173, 0.71023596752501739, 0.8625152869878786, 0.19022506746859158, 0.87195203613890515, 0.52223737867131592, 0.87889200248158028, 0.89802770436521395]
Plot the simulated and fit tuning curves¶
plt.figure(figsize=[15, 15])
for neuron in range(pop.n_neurons):
plt.subplot(4, 3, neuron + 1)
pop.display(x_test, Y_test[:, neuron], neuron=neuron,
ylim=[0.8 * np.min(Y_test[:, neuron]), 1.2 *
np.max(Y_test[:, neuron])])
plt.show()
Decode feature from the population activity¶
xhat_test = pop.decode(Y_test)
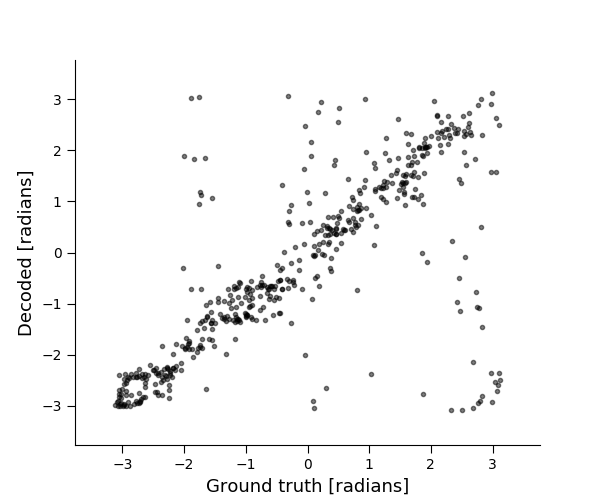
Visualize ground truth vs. decoded estimates¶
plt.figure(figsize=[6, 5])
plt.plot(x_test, xhat_test, 'k.', alpha=0.5)
plt.xlim([-1.2 * np.pi, 1.2 * np.pi])
plt.ylim([-1.2 * np.pi, 1.2 * np.pi])
plt.xlabel('Ground truth [radians]')
plt.ylabel('Decoded [radians]')
plt.tick_params(axis='y', right='off')
plt.tick_params(axis='x', top='off')
ax = plt.gca()
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
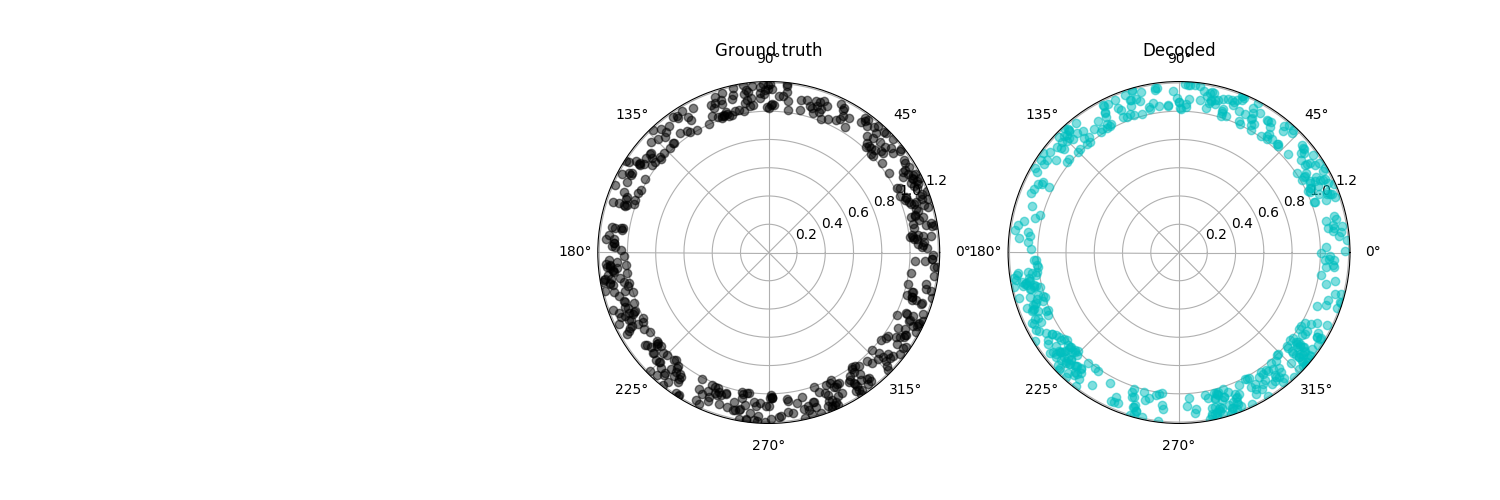
plt.figure(figsize=[15, 5])
jitter = 0.2 * np.random.rand(x_test.shape[0])
plt.subplot(132, polar=True)
plt.plot(x_test, np.ones(x_test.shape[0]) + jitter, 'ko', alpha=0.5)
plt.title('Ground truth')
plt.subplot(133, polar=True)
plt.plot(xhat_test, np.ones(xhat_test.shape[0]) + jitter, 'co', alpha=0.5)
plt.title('Decoded')
plt.show()
Score decoding performance¶
# Circular correlation
circ_corr = pop.score(x_test, xhat_test, method='circ_corr')
print('Circular correlation: %f' % (circ_corr))
Out:
Circular correlation: 0.743451
# Cosine distance
cosine_dist = pop.score(x_test, xhat_test, method='cosine_dist')
print('Cosine distance: %f' % (cosine_dist))
Out:
Cosine distance: 0.797382
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 22.722 seconds)